- To Calculate Liner Length:
- L = Max Length + Twice Depth + 3’
- To Calculate Liner Width:
- W = Max Width + Twice Depth) + 3’
- Pond Opening: 10’ Long, 8’ Wide, 2’ Deep:
- Calculate Length: 10’ + 2(2’) + 3’ = 17’
- Calculate Width: 8’ + 2(2’) + 3’ = 15’
- Volume For Average Pond:
- WIDTH x LENGTH x Depth = Cubic Feet
- Cubic Feet x 7.5 = GALLONS
- Volume For Circular Pond:
- RAD x RAD x 3.14 x DEPTH = Cubic Feet
- Cubic Feet x 7.5 = GALLONS
- Knowing Gallons Helps With:
- Sizing Pump, Adding Treatments, Sizing Filter, Stocking Fish
- Perfect Rectangle:
- EX: 11’ x 16’ x 2’ – 352 Cu. Ft.
- 352 (cubic feet) x 7.5 gal = 2640 gallons
- Boulders In Pond:
- Pond Length x Pond Width ÷ 65 = _______ Tons
- Rocks In Pond:
- Tons Of Boulders x .45 = _______ Tons
- Boulders In Stream:
- Every 10’ = ¾ Ton
- Rocks In Stream:
- Every 10’ Section = ½ Ton
- Components:
- Underlayment, Liner
- Submersible Pump
- Skimmer
- Waterfall Filter
- Options:
- Underwater Lights
- Transformer UV Clarifier Plants
- If average depth is greater than 2’, consider one of the following:
- Bottom Suction
- Bottom Drain
- Vacuum Bottom Drain
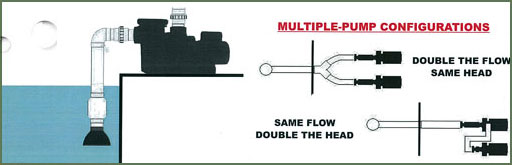
- WEIR WIDTH x 150 GPH – PUMP SIZE*
- EX: 36” Weir x 150 GPH = 5400 GPH
- Rule Of Thumb:
- Reservoir should hold 2 to 3 times amount of water in stream & falls.
- Water In A Pump Vault:
- Rule of thumb: 40% Water, 60% Rock
- Water Volume In Stream Bed:
- Stream EX: 3’ Wide x 20’ Long
- 3’ x 20’ x .33 x 7.5 = 148.5 Gallons
- Approximately 150 gallons in stream.
- Basin matrix can replace up to 90% of gravel that is traditionally placed in pond free reservoirs.
- They have up to 3 times more storage capacity than gravel.
- Allows for smaller reservoir.
- Easier to maintain water levels.
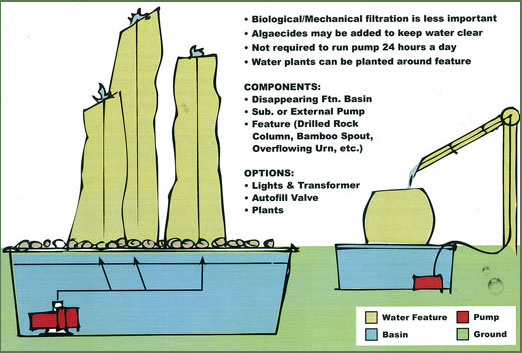
- Biological filtration is less important.
- Mechanical filtration is less important.
- Algaecides may be added to keep water clear.
- Not required to run pump 24 hours a day.
- Components:
- Underlayment
- Liner Pump Vault
- Submersible Pump
- Matrix Box(es)
- Waterfall Weir
- Options:
- Underwater Lights & Transformer
- Autofill Valve
- Plants
- Aids in drawing debris missed by skimmers.
- Draw water from the bottom and allow the entire water column to be filtered.
- Work to draw water in rocked ponds but are ideal in smooth sloped bottoms.
- Ang. 4” BD = 6’ Sweeping Radius
- Aerated bottom drains help increase the effectiveness of a sweeping action
Cover pond with leaf netting to keep out leaves and debri and birds of prey. Check your fish carefully for parasites and bacterial infections and take appropriate action before winter close up. Do not let pond freeze solid, always keep a small area open to let the gasses exchange Example ( floating pond heater) or aeration pump with diffuser stone. Do not chop a hole in the ice, because the sound waves can affect your fish health
Temperature of water in pond – When water temperature is above 55f koi will swim and start to feed normal. When temperature falls below 50f koi begin to slow down and hibernate. At this point do not feed. Provide a natural refuge for your pond fish while they are inactive by placing large diameter plastic or terra-cotta pipe 6” wide or more.
Remember shutting down your pond pump and filtration systems in the winter months vary due to what type of pumps external or submersible. Filtration systems also vary to what type of filters whether they are in the ground filters or above ground systems. If your system requires shut down for the winter months, make sure water is drained in plumbing lines and filters and pumps.
In the most general terms, pond algae can be divided into two types: Single Cell & String Algae.
- Single Cell Algae:
- Microscopic single cell algae causes pong water to turn a pea soup, green color. They will appear when nutrients, sunlight, and water are present. They are so small that it is not possible to simply “filter” them out of pond water.
- Methods of Removal:
- Flocculants
- Reduce Food Source
- Ben. Bacteria & Plants Help by Reducing Nutrients Needed for Algae to Survive
- UV Clarifiers
- Algaecide
- String/Filamentous Algae:
- String algae often appear in clear pond water. It attaches itself to rock in streambeds and waterfalls. Also to sides of rocks inside pond. Blanketweed is another form of string algae. It rises to the surface of pond during heat of the day and stinks when water cool.
- Methods Of Removal:
- Products That Remove Organic Debris
- Algaecide
- Brush/Twister
- Pond Vacuum
- Suggested Plant Coverage: 1/3 to ½ surface area coverage
- Increased Plant Load: Yields increased Oxygen (DO) during the day, but too much plant load can cause oxygen deprivation at night. Especially dangerous for ponds with high fish & high plant loads.
- Low Plant Load: Yield increased nitrated (fertilizer) which increases the likeness for algae.
- Water Lilies:
- Tropical (Fragrant): Day Blooming, Night Blooming
- Hardy
- Lotuses:
- Traditional
- Miniature (“Bowl” Lotuses)
- Submerged (“Oxygenators”):
- Anacharis
- Hornwort
- Cabomba
- Floaters:
- Water Hyacinth
- Water Lettuce
- Azolla
- Duckweed
- Frogbit
- Marginal (“bog” plants):
- Hardy: Cattail, Iris, Sweetflag
- Tropical: Giant Papyrus, Umbrella Palm, Water Canna
- General Pond Tips:
- 80 °+ - Increase pump circulation OR add air pump
- 75 °+ - Fertilize aquatic plants 2X per month
- 70°+ - Add tropical aquatic plants to pond
- 60°+ - Begin fertilizing aquatic plants
- 50°+ - Begin using bacteria treatments, Re-pot aquatic plants (Spring)
- 50°- - Cut back aquatic plants (Fall)
- 45°+ - Start pumps & filters for season
- 45°- - Keep opening in ice
- General Fish Feeding Tips:
- Feed only as much food as fish can consume in 5 minutes.
- Above 65°: Feed color enhancing & high protein food.
- 65° & Below: Feed wheat germ food (Spring, Fall, & Winter)
- Ice Opening Tips:
- Cold climates: De-Icer(s)
- Mild climates: Airstones
- Feeding Rates:
- As much food that can be consumed in 5min
- ≤8” = 5% of body weight daily
- ≥8” = 2% of body weight daily
- Possible to overfeed fish, but more than likely overfeed the filter from decomposing food
- Most important time for fish growth rate is up to 2 years of age
- Types Of Food:
- Easily Digested: Spring & Fall (wheat germ)
- Standard Diets: Complete nutrition
- Color Enhancing (spirulina): Develop beauty & distinct coloration
- Growth Diets (high protein): Helps quickly add weight and girth
- Advanced Diets: Deneficial bacteria added to food
- Common Guidelines:
- Quality food reduces fish waste in water
- More easily digested
- Never overfeed
- It is better to feed less than too much
- Remove leftover food immediately
- Sudden temperature change: Stop feeding or reduce until normal again
- pring feeding: Use easily digested diets (wheat germ)
- Stop Feeding: Water temperature below 50°
- Early Fall: High protein diet for winter storage
- Late Fall: Use easily digested diets (wheat germ)



